QLED vs. UHD: Which TV Technology Is Better in 2026?
Summary: UHD (Ultra High Definition) strictly denotes a resolution standard of 3840 x 2160 pixels, focusing on delivering sharper details and crisper text through higher pixel density. In contrast, QLED is a specific display panel technology that utilizes a "Quantum Dot" layer to significantly enhance brightness (often exceeding 1,500 nits) and color volume for more vibrant visuals. While frequently compared, these terms are not mutually exclusive; most QLED TVs are essentially UHD 4K panels enhanced with Quantum Dot technology, combining the high resolution of UHD with the superior color performance of QLED.
Table of Contents
Shopping for a new TV can be confusing when acronyms like LED, LCD, QLED vs UHD show up together. QLED and UHD appear especially often because both are marketed heavily for gaming and movie watching, but many people are unsure how they differ or what each one actually offers.
The truth is, QLED refers to panel technology, while UHD refers to resolution. In many cases, a TV can be both QLED and UHD. It may seem confusing, but don't worry. This guide explains the terms, clears up the confusion, and gives test-based advice on when to choose a UHD TV or a QLED model.

What is QLED?
Definition of QLED

QLED (Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diode) refers to an LCD TV that uses an LED backlight together with a layer of quantum dots. These tiny particles sit in front of the backlight and convert blue light into very specific shades of red and green. Because the colors coming from this layer are cleaner and more controlled, QLED TVs tend to show brighter highlights and more vivid color, particularly in well-lit scenes.
Features, Strengths and Limitations of QLED
QLED screens deliver value beyond just sharper resolution: with their quantum-dot layer, they push brightness and color vibrancy much higher than standard LED-LCD sets, often supporting HDR10+ or HLG for more realistic lighting and richer tones. Many recent Samsung models combine 4K (and in some cases 8K) resolution with smart features like low-lag gaming (4K120), HDMI 2.1 support, and streaming app compatibility, plus ambient/voice assistant tools to ease usability. In well-lit spaces or for vivid daytime viewing, QLED screens shine. Still, if your priority is flawless contrast, deep blacks, and pristine off-angle viewing — especially in a dark room — something like OLED or a top-tier panel with very strong local dimming might outperform.
Strengths of QLED
- Modern QLED screens can reach very high HDR peaks. (For example, according to Tom's Guide, Samsung's Neo QLED QN90D measured around 2,024 nits in Filmmaker Mode.)
- Great in bright rooms since it holds up well against glare and stays colorful.
- Well-established tech because quantum-dot TVs have been refined over many years.
Limitations of QLED
- Still uses a backlight, so blacks aren't as deep as OLED.
- Bright objects in dark scenes can show a halo (blooming).
- Side viewing can look washed out on some models.
What is UHD?
Definition of UHD
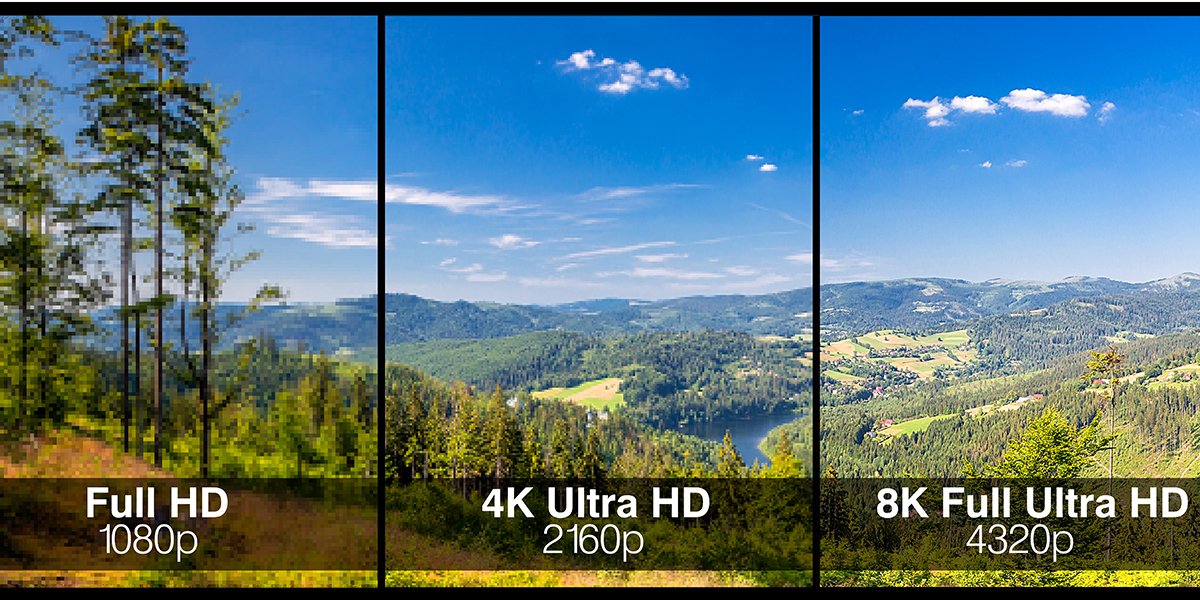
UHD (Ultra High Definition) describes resolution. In other words, unlike QLED, which refers to display technology, UHD is about the number of pixels on the screen. This means you can have a UHD TV that uses QLED, OLED, or LED-LCD panel technology. Most 4K UHD TVs are 3840×2160, which is four times 1080p. The next step up is 8K at 7680×4320. According to the Global Growth Insights, over 85% of TV sets sold today support 4K UHD resolution, reflecting the technology's rapid market penetration.
Features, Strengths and Limitations of UHD
UHD increases the number of pixels on the screen, allowing small details to appear clearer. With true 4K content such as UHD Blu-ray, edges and textures look cleaner compared with lower-resolution formats. Still, resolution is only one factor in image quality. UHD does not influence brightness, contrast, or color performance; those aspects depend on the panel, backlight system, and the TV's processing capabilities.
Strengths of UHD
- Sharper fine detail (hair, grass, fabric textures look more defined vs 1080p).
- Crisper edges & text with fewer "jaggies" at normal seating distances.
- Bigger screens without visible pixel.
- Greater perceived depth from finer spatial detail on close-to-screen viewing.
Limitations of UHD
- Resolution alone ≠ picture quality; without good upscaling/HDR/contrast, 4K can still look flat.
- Diminishing returns on small screens or long seating distances.
QLED vs UHD: Comparison Chart

Before we dive into QLED vs UHD comparison, it's important to be clear that QLED and UHD aren't directly comparable because they refer to different things:
- QLED is a display technology developed by Samsung.
- UHD refers to a resolution standard.
In fact, most QLED TVs are also UHD TVs, which means that you're choosing between a QLED display with UHD resolution and another panel with the same resolution (such as a standard LED or OLED). If you find yourself debating whether to pick a QLED vs a UHD TV, the table below lays out the key differences, helping you decide which features matter most for your viewing setup.
| Similarity & Difference between UHD vs QLED | ||
| Features | QLED TV | UHD TV |
| Definition | Display technology using quantum dots | Resolution standard (4K or 8K) |
| Resolution | Most QLED models are 4K (some 8K), so you often see QLED and UHD together. | 4K/8K regardless of whether the TV is QLED, OLED, or standard LED-LCD. |
| Strengths |
Bright, vivid color with higher color accuracy and strong peak brightness |
Higher pixel count delivers sharper, crisper detail |
|
Connectivity |
Both typically supports HDMI 2.0/2.1, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth. |
|
|
Smart TV features |
Both usually come with smart operating systems, voice assistant compatibility, and streaming apps like Netflix, and more. | |
| Performance vs OLED | Brighter but less deep blacks | Depends on the panel type used |
| Ideal Use | Bright rooms, vibrant visuals |
Large screens, detail-rich content |
| Price | Higher due to added quantum-dot/mini-LED tech. | More affordable across sizes/brands. |
Which One Should You Choose, QLED vs UHD?
When choosing between UHD TVs vs QLED TVs, the key information you must understand is that almost all modern TVs, whether LED or QLED, are UHD. However, not all UHD TVs are QLED.
The table above already highlights the different areas of focus between the two concepts. We suggest you choose based on your viewing needs. Below are some recommendations we've summarized after testing in a variety of environments:
For Bright Rooms and Vibrant Visuals:
Prioritize a high-brightness QLED/Mini-LED with strong anti-glare and local dimming. Recent picks tested for bright-room punch include Samsung Neo QLED QN90D/QN90F and TCL C8K; both are reviewed for very high HDR peaks and solid glare handling.
For Gamers Looking for Performance:
Both UHD and QLED TVs support 4K gaming, but QLED TVs often include features like faster refresh rates and HDMI 2.1 support. The Samsung Q80T or TCL 6-Series are popular choices among gamers.
For Budget-Conscious Buyers:
Entry-level UHD 4K models deliver sharp detail but may lack higher peak brightness or advanced gaming features. Examples like LG UT8000 illustrate the trade-off: low input lag but 60 Hz-only and no VRR. Step up to mid-range Mini-LED/QLED (e.g., Hisense/ TCL U-/C-series) if you want more HDR impact.
For Movie Nights in a Dark Room:
UHD (4K) gives the detail baseline; perceived contrast depends on the backlight and local-dimming quality. Bright-room champs aren't always the best in dark scenes—use bright-room and overall quality rankings together when choosing.
For Signage or Display Use:
If sharp text and clean detail are the priority, such as for menus, product displays, or presentations, UHD resolution is what matters most. For more eye-catching colors or high-impact visuals, QLED models tend to offer stronger brightness and richer color reproduction.
Final Verdict:
- Choose a QLED TV if you want stronger brightness and color performance and don't mind spending a bit more.
- If you mainly need clear 4K resolution at a lower price, a standard UHD model from brands like LG, Sony, Hisense, or TCL will serve you well.
Can UHD TVs Play 4K UHD Blu-ray Movies?
Yes, UHD TVs can show the full detail of 4K Ultra HD Blu-ray movies, but they still require a separate 4K UHD Blu-ray player. A few premium TVs include built-in disc hardware, though most models do not, so an external player is usually needed.
If you prefer not to rely on a standalone player, another option is to convert your 4K UHD Blu-ray discs into digital video files. These files are easy to store, access, and play across a wide range of devices. You can even save them to an external drive or cloud storage. That's where DVDFab UHD Ripper comes in, allowing you to extract 4K UHD Blu-rays and convert them to high-quality digital files to enjoy movies on your UHD or QLED TV.
Frequently Asked Questions
LED and QLED are display technologies for TVs and monitors.
LED (Light Emitting Diode) uses light-emitting diodes to illuminate pixels, offering good color accuracy and contrast ratios, with edge-lit and full-array types available.
QLED (Quantum Dot LED), developed by Samsung, adds quantum dots to an LED TV enhancing color gamut, brightness, and overall picture quality.
For affordability with good image quality, choose LED; for superior colors and brightness at a higher cost (with potential burn-in risk), consider QLED.
These are not competing features. Most QLED models use a 4K UHD panel, so the distinction isn't about one being “better.” QLED refers to the panel’s color and brightness technology, and many QLED sets tend to look brighter and more saturated than basic UHD LCD models.
Does QLED support HDR?
Yes. Most QLED TVs work with common HDR formats such as HDR10, HDR10+, or Dolby Vision, depending on the brand. HDR performance still varies by model, but QLED sets generally have the brightness needed to show HDR highlights effectively.
What does the future hold for QLED and UHD TV technologies?
Both QLED and UHD technology are constantly evolving. Newer QLED models use more advanced quantum-dot materials and better backlight systems, while UHD panels are now available across a wider range of screen sizes and price levels. Technologies like Mini-LED and MicroLED are also becoming more common, offering higher contrast and more precise lighting control. Although 8K UHD exists, 4K remains the main format for most content.
Conclusion
Choosing between QLED and UHD comes down to understanding what each one contributes to picture quality. Most QLED models already use a UHD panel, so the decision is less about picking one over the other and more about matching a TV to the way you watch content. Look at factors such as brightness, contrast control, and gaming features before deciding.
If you want to play 4K UHD Blu-ray movies but do not use a disc player, you can convert your discs into digital files with tools like DVDFab UHD Ripper and play them directly on your TV.