What is a DVD? How to Easily Backup Protected DVDs?
Summary: DVDs are a type of optical disc that is used to store data. DVDs differ from CDs in a few ways. This article will cover some important differences between these two optical disc media types and provide a guide for backing up your protected DVD content. So, read on to learn more about what is a dvd?
Table of Contents
You've probably seen DVDs on store shelves or in old media libraries, but have you ever stopped to ask: what exactly is a DVD? A DVD is an optical format designed to hold far more data than its predecessor, the CD (Compact Disc). While DVDs once dominated home entertainment, streaming services now carry much of that load. If you still own a DVD collection, it's wise to think about backing it up and protecting it. In this article I'll walk through what a DVD is, how it differs from a CD, and how you can back up even protected discs to keep your media safe for years to come.
What is a DVD?
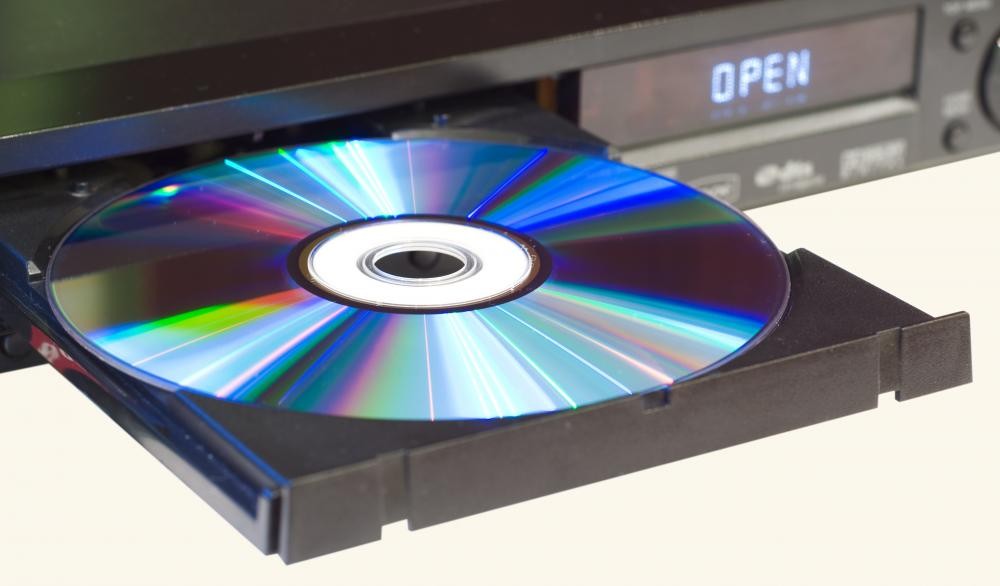

A DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) is an optical disc format used to store data, movies, and music. It evolved from the CD format, offering higher capacity and better audio-visual quality. Introduced in 1995, DVDs quickly became the global standard for video distribution and computer data storage.
Each disc is made of clear polycarbonate plastic with one or more reflective metal layers inside. A laser reads tiny pits arranged in a spiral track to retrieve the stored data. A single-layer DVD can hold about 4.7 GB, while a dual-layer disc can store up to 8.5 GB, enough for a full-length movie and bonus features.
Beyond home entertainment, DVDs are widely used for software installation, data backup, and video archiving. Although they share a similar size and appearance with CDs, DVDs use a narrower laser beam.
The Difference Between a CD and a DVD

Once you understand what does DVD stand for, it's easier to see how it evolved from the CD. Both are optical discs designed to store digital data, yet they differ in capacity, purpose, and technology.
The Compact Disc (CD) was introduced in 1982 as the first consumer optical storage medium. Originally designed for music playback, it stores data using a spiral track of microscopic pits read by an infrared laser. A DVD, released more than a decade later, built on this foundation by using more densely packed data tracks. This design allowed for far greater capacity and made DVDs suitable for full-length movies and large data files.
CD vs. DVD: Key Differences
| Feature | CD | DVD |
| Storage Capacity | 700 MB | 4.7 GB (single-layer) / 8.5 GB (dual-layer) |
| Main Usage | Audio, software, and small data files | Movies, backups, software, and large data storage |
| Resolution & Quality | Standard-definition audio and data | Supports higher video and audio quality |
| Laser Technology | Infrared laser (780 nm) | Red laser (650 nm) with tighter data spacing |
| Data Transfer Speed | Slower | Faster read and write speeds |
| File Formats | MP3, WAV, ISO | MPEG-2, VOB, AC3, DTS, ISO |
| Compatibility | Works with nearly all CD players and computer drives | Requires DVD-capable players or DVD drive |
| Durability | Less data density, slightly more resistant to surface damage | Higher density, may need careful handling |
DVDs became the preferred choice for movies, archives, and large file backups thanks to their higher capacity and improved playback quality. Today, even as streaming dominates, DVDs still offer collectors and archivists a long-lasting storage option.
Overview of DVD Types and Their Uses

DVDs are available in several formats, each created for specific recording and storage purposes. Understanding these variations helps you choose the right disc for your needs.
| DVD Type | Description | Typical Uses |
| DVD-ROM (Read-Only Memory) | Pre-recorded discs produced in bulk by manufacturers. The data cannot be changed or erased. | Commercial movies, video games, and software releases. |
| DVD-R (Recordable) | Write-once discs that allow users to record data, audio, or video a single time. | Archiving data or creating personal movie collections. |
| DVD-RW (Rewritable) | Can be erased and re-recorded multiple times. | Temporary backups, repeated testing, or media drafts. |
| DVD+R (Recordable) | Similar to DVD-R but uses a different writing method that often improves compatibility and reliability. | Video recording and long-term data storage. |
| DVD+RW (Rewritable) | A rewritable version of DVD+R that supports multiple write/erase cycles. | Projects requiring frequent file updates. |
| DVD-R DL (Dual Layer Recordable) | Contains two data layers, nearly doubling storage capacity. | Extended movies, large archives, or high-quality video projects. |
| DVD+R DL (Dual Layer Recordable) | Uses the +R format but with dual layers, often yielding faster writing and better playback compatibility. | Long-form video and high-capacity storage. |
| DVD-RAM (Random Access Memory) | Functions more like a hard drive, with random read/write access and excellent durability. | Professional video recording and reliable long-term backups. |
| Mini DVD | Smaller 8 cm discs (compared to the standard 12 cm DVD size). | Common in older camcorders and some portable DVD players. |
Each DVD format offers a different balance between capacity, rewrite flexibility, and playback compatibility. For long-term archives or professional use, DVD-RAM and dual-layer discs are preferred, while DVD-R or DVD+R remain popular for personal backups and home video projects.
How to Backup Protected DVDs Using DVDFab DVD Copy?
DVDFab DVD Copy is an user-friendly tool to back up both protected and unprotected DVDs. The program removes common protection systems such as CSS, RC, RCE, APS, and Sony DADC, allowing you to create playable backups without errors. Thanks to GPU acceleration and batch processing, even large collections can be copied efficiently.
- Full Disc: This mode copies the entire DVD, including menus and special features.
- Main Movie: This mode copies only the main movie without any extras.
- Split: This mode lets you split a DVD-9 into two blank discs.
- Customize: This mode allows you to choose specific titles or chapters to copy from the source DVD.
- Merge: This mode enables you to combine two or more DVDs into one.
- Clone/Burn: This mode lets you clone your DVD in a 1:1 ratio or burn it to a blank disc.
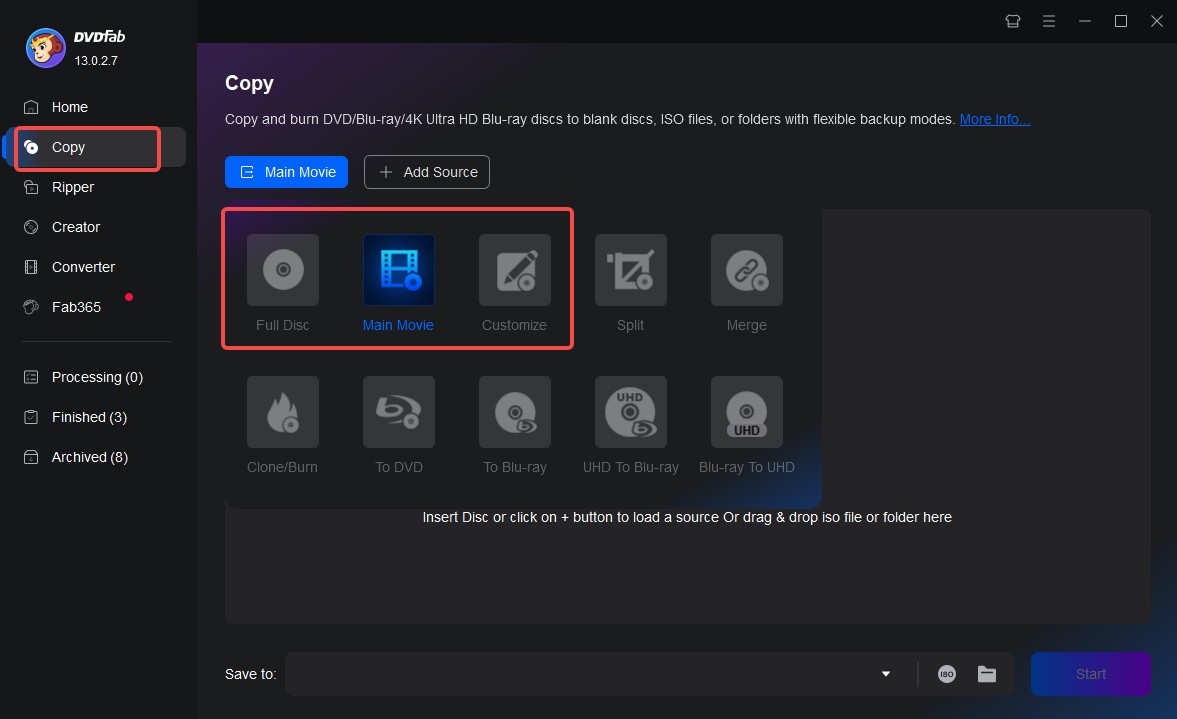
How to Use DVDFab DVD Copy to Back Up Your DVD
Step 1: Download and Install DVDFab
Begin by downloading and installing this DVD decrypter on your computer. You can obtain it from the official website or click the download button below.
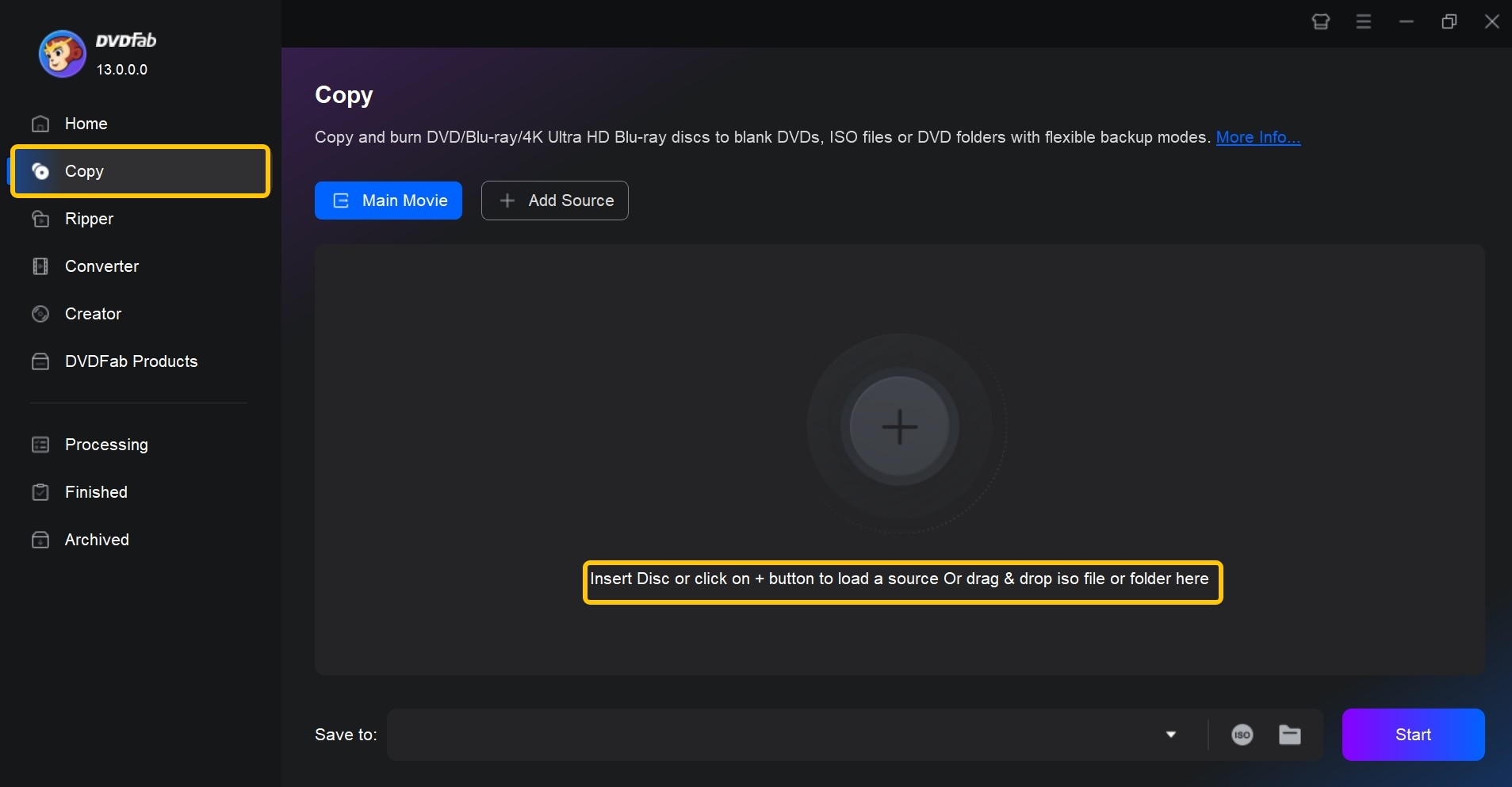
Step 2: Load the DVD Source
Once installed, open the program and switch to the Copy module. Then, insert the DVD into your optical drive. The software will detect it automatically. You can also click "+" to load the disc manually, or drag and drop an ISO/DVD folder into the main interface.
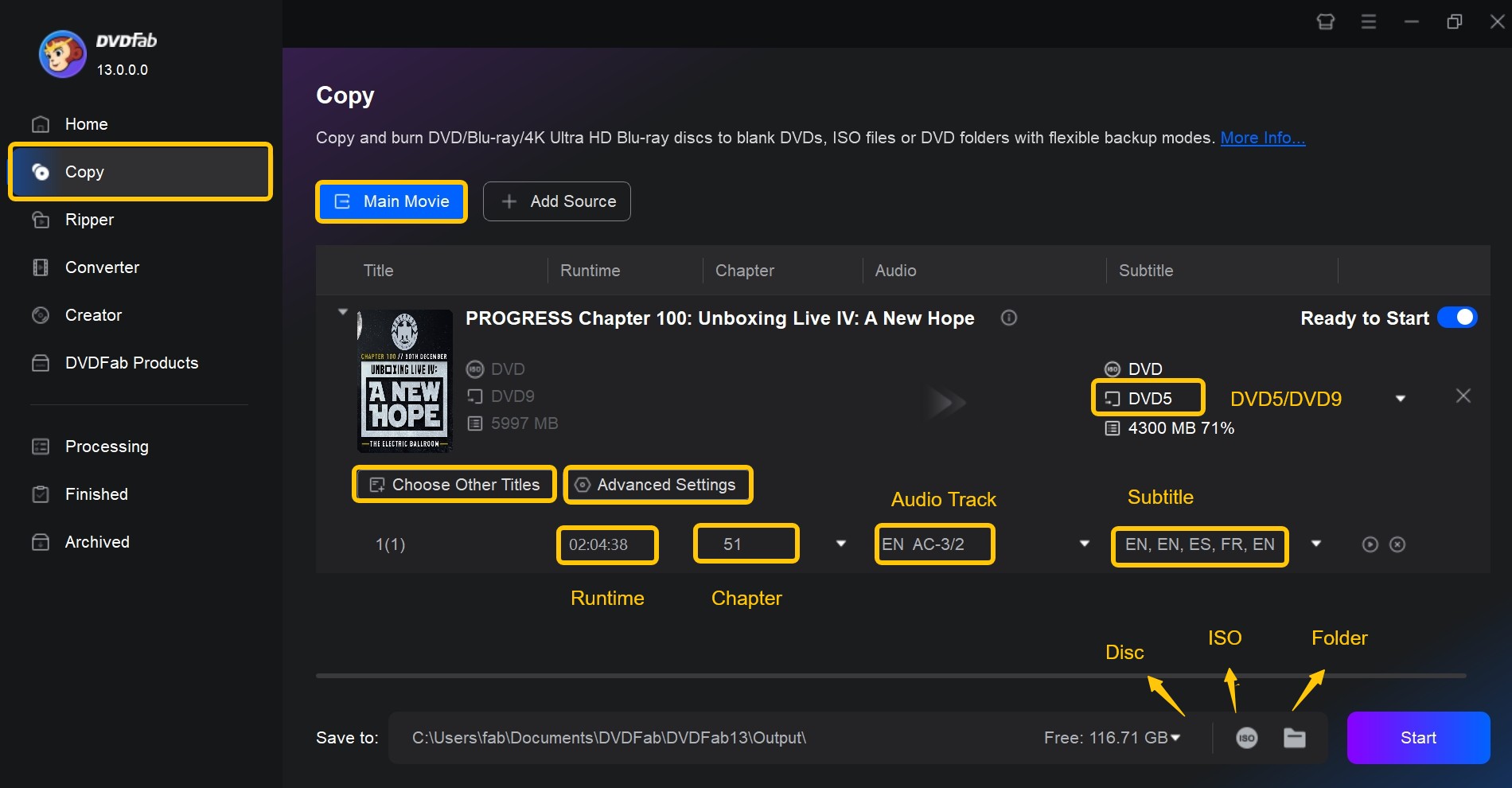
Step 3: Choose a Copy Mode and Customize the DVD
Now, select a copy mode from the six available options. After choosing, you can customize the backup by selecting specific chapters, audio tracks, and subtitles. If you're creating a digital backup, you can save the file as an ISO image or VIDEO_TS folder.
Step 4: Start Copying
Once you've completed the customization, click the "Start" button to begin copying your DVD. Progress and remaining time are displayed, and you can pause or cancel at any moment.

💡Related reading: What is streaming?
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. This DVD copy protection removal software can remove most types of disc protection, including CSS, RC, APS, Sony DADC, and RCE. It can also bypass Cinavia watermarks to produce clean, playable copies. With its built-in decryption engine, the program allows you to create either a lossless 1:1 copy or a compressed backup that preserves high video and audio quality.
Making a personal backup of DVDs that you legally purchased is generally allowed in many regions under fair use or personal use exceptions. However, removing copy protection or sharing those copies online can violate copyright laws in some countries, such as the United States. It is advisable to check local regulations before copying any DVD content.
Both DVD-R and DVD+R are recordable formats, but they use different writing standards:
- DVD-R allows you to record data once. After burning, the content cannot be erased or rewritten.
- DVD+R follows an alternative format that often improves writing accuracy and playback compatibility with newer drives.
If you need to rewrite discs multiple times, choose DVD-RW or DVD+RW instead, which support repeated writing and erasing.
The Bottom Line
A DVD is more than just a movie disc. It's one of the most influential forms of optical storage in digital history. It bridged the gap between physical and digital media, offering a durable and affordable way to preserve data and entertainment. Even as streaming dominates today's media landscape, understanding what a DVD is and how to keep your collection safe remains valuable. Whether you keep your discs for nostalgia or practical archiving, tools like DVDFab make it easy to convert your DVD to MP4 and other digital formats.

![How to Convert DVD to MP4: 14 Tools Tested & Guide [2026]](https://r3.dvdfab.cn/upload/resource/convert-dvd-to-mp4-p2X3.jpeg)

![How to Convert DVD to AVI Free and Easily [2026 Updated]](https://r6.dvdfab.cn/upload/resource/en/dvd-to-avi-QL6y.jpg)
![10 Best DVD Rippers for Windows & macOS [2026 Expert Review]](https://r2.dvdfab.cn/upload/resource/en/best-free-dvd-ripper-bQ7P.jpg)